The impact of transformation policies on the resilience of mining resource-based cities
-
摘要: 资源型城市由于产业结构单一、生态环境恶化、社会风险突出等问题,韧性普遍不足。在全面推进高质量发展的战略背景下,客观评价转型政策对资源型城市韧性的影响,对降低城市风险、补齐政策短板意义重大。基于2006—2020年278个地级市的面板数据,采用PSM-DID方法构建双向面板固定效应模型,考察《全国资源型城市可持续发展规划(2013—2020年)》在推进资源型城市转型中对城市韧性的影响,并进行实证分析。研究发现:《规划》对改善城市韧性具有显著促进作用,但存在政策滞后性;机制分析表明,《规划》主要通过优化产业结构和改善住房条件促进城市韧性水平提高;异质性分析表明,不同类型资源型城市的政策效果存在明显差异,其中衰退型资源型城市韧性的改善效果最为显著。Abstract: Problems like a lack of diverse industries, environmental degradation and major social risks can lead to low resilience in resource-based cities.As part of a broader strategy to achieve high quality development, it therefore remains imperative to objectively assess the effects of transformation policies on the resilience of these cities.This will help to minimize urban risks and fill gaps in policy making.Based on the panel data of 278 prefecture-level cities from 2006 to 2020, this study proposed a two-way panel fixed-effects model using the PSM-DID method to examine the impact of the National Plan for Sustainable Development of Resource-based Cities(2013-2020) on urban resilience in promoting the transformation of resource-based cities.Through the present empirical analysis, we found that: the Plan does have a significant role to play in boosting urban resilience, but there is a policy lag; the mechanism analysis shows that the Plan raises urban resilience level mainly through optimizing industrial structure and improving housing conditions; the heterogeneity analysis shows that there are significant differences in the policy effects on different types of resource-based cities, among which declining resource-based cities exhibit the most significant improvement in their urban resilience.
-
Key words:
- mining resource-based cities /
- transformation policies /
- urban resilience /
- policy evaluation /
- PSM-DID
-
表 1 PSM匹配结果
Table 1. PSM matching results
样本 未匹配样本 匹配样本 总计 控制组 186 2 364 2 550 实验组 0 1 620 1 620 总计 186 3 984 4 170 表 2 倾向得分匹配前后样本平衡性检验结果
Table 2. Results of sample balance test before and after propensity score matching
匹配方法 伪R2 LR统计量 标准化偏差/% 匹配前 0.097 542.44 29.9 马氏距离匹配 0.001 6.72 1.4 最近相邻匹配 0.002 7.88 2.8 卡尺(半径)匹配 0.002 10.48 3.8 卡尺内最近相邻匹配 0.002 10.48 3.8 核匹配 0.002 6.77 3.1 表 3 基准回归估计结果
Table 3. Baseline regression estimation results
变量 M1 M2 M3 M4 效应系数 0.009** 0.022*** 0.023*** 0.025*** (0.003) (0.002) (0.003) (0.004) 控制变量 否 是 是 是 C 否 否 是 是 Y 否 否 否 是 R2 0.50 0.55 0.55 0.56 N 3 984 3 984 3 984 3 984 注:括号内为标准误差;*** P < 0.01;** P < 0.05。 表 4 改变政策冲击时间的检验结果
Table 4. Test results for changing the timing of policy shocks
变量 M5(2010) M6(2011) M7(2012) 效应系数 0.003 0.003 0.003* (0.002) (0.002) (0.002) 控制变量 是 是 是 C 是 是 是 Y 是 是 是 R2 0.61 0.61 0.61 N 3 984 3 984 3 984 注:*P<0.1。 表 5 影响机制检验结果
Table 5. Results of impact mechanism test
变量 M8 M9 M10 con R sta R inv R 效应系数 0.034** 0.024*** -0.031** 0.023*** 1.477*** 0.025*** (0.032) (0.004) (0.033) (0.004) (0.195) (0.003) con — 0.015*** — — — — — (0.007) — — — — sta — — — 0.004** — — — — — (0.007) — — inv — — — — — 0.071*** — — — — — (0.007) 控制变量 是 是 是 是 是 是 C 是 是 是 是 是 是 Y 是 是 是 是 是 是 R2 0.643 0.603 0.717 0.586 0.755 0.646 N 3 984 3 984 3 984 3 984 3 984 3 984 表 6 不同类型城市的异质性检验结果
Table 6. Heterogeneity test results for different types of cities
变量 M11
(成长型)M12
(成熟型)M13
(衰退型)M14
(再生型)效应系数 0.004** 0.012** 0.041*** 0.004 (0.004) (0.002) (0.002) (0.003) 控制变量 是 是 是 是 C 是 是 是 是 Y 是 是 是 是 R2 0.522 0.563 0.644 0.115 N 2 106 3 201 2 256 2 680 -
[1] 陈玉梅, 李康晨. 国外公共管理视角下韧性城市研究进展与实践探析[J]. 中国行政管理, 2017(1): 137-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXGL201701025.htmChen Yumei, Li Kangchen. Overseas studies progress and practice exploration on resilient city—based on the perspective of public administration[J]. Chinese Public Administration, 2017(1): 137-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXGL201701025.htm [2] 朱正威, 刘莹莹, 杨洋. 韧性治理: 中国韧性城市建设的实践与探索[J]. 公共管理与政策评论, 2021, 10(3): 22-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGZC202103004.htmZhu Zhengwei, Liu Yingying, Yang Yang. Resilient governance: practice and exploration of urban resilience building in China[J]. Public Administration and Policy Review, 2021, 10(3): 22-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGZC202103004.htm [3] 孙天阳, 陆毅, 成丽红. 资源枯竭型城市扶助政策实施效果、长效机制与产业升级[J]. 中国工业经济, 2020(7): 98-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYY202007007.htmSun Tianyang, Lu Yi, Cheng Lihong. Implementation effect of resource exhausted cities' supporting policies, long-term mechanism and industrial upgrading[J]. China Industrial Economics, 2020(7): 98-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYY202007007.htm [4] 谭玲玲, 肖双. 基于全要素生产率视角资源型城市低碳转型效果评价模型[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(2): 58-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201802011.htmTan Lingling, Xiao Shuang. Evaluation model of resource-based cities' low-carbon transition effect based on total factor productivity[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(2): 58-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKA201802011.htm [5] 卢硕, 张文忠, 李佳洺. 资源禀赋视角下环境规制对黄河流域资源型城市产业转型的影响[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2020, 35(1): 73-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX202001012.htmLu Shuo, Zhang Wenzhong, Li Jiaming. Influence of environmental regulations on industrial transformation of resource-based cities in the Yellow River Basin under resource endowment[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 35(1): 73-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX202001012.htm [6] 彭飞, 金慧晴. 区域产业政策有效性评估: 基于中国资源型和老工业城市的证据[J]. 产业经济研究, 2021(3): 99-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJJ202103008.htmPeng Fei, Jin Huiqing. An effectiveness evaluation of regional industrial policy: based on evidence from resource-based and old industrial cities in China[J]. Industrial Economics Research, 2021(3): 99-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJJ202103008.htm [7] 高志刚, 李明蕊. 制度质量、政府创新支持对黄河流域资源型城市经济高质量发展的影响研究——基于供给侧视角[J]. 软科学, 2021, 35(8): 121-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XUXI202108018.htmGao Zhigang, Li Mingrui. Research on the influence of system quality and government innovation support on the high-quality economic development of resource-based cities in the Yellow River Basin: based on the supply-side perspective[J]. Soft Science, 2021, 35(8): 121-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XUXI202108018.htm [8] 周宏浩, 谷国锋. 资源型城市可持续发展政策的污染减排效应评估: 基于PSM-DID自然实验的证据[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(10): 50-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202010008.htmZhou Honghao, Gu Guofeng. Assessment on pollution reduction effects of sustainable development policy in Chinese resource-based cities[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(10): 50-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202010008.htm [9] 郑飞鸿, 李静. 科技环境规制倒逼资源型城市产业转型升级: 理论模型与双重效应分析[J]. 软科学, 2021, 35(12): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XUXI202112004.htmZheng Feihong, Li Jing. Industrial transformation and upgrading of resource-based cities forced by technological environmental regulation: based on theoretical model and double effect analysis[J]. Soft Science, 2021, 35(12): 22-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XUXI202112004.htm [10] 张艳, 郑贺允, 葛力铭. 资源型城市可持续发展政策对碳排放的影响[J]. 财经研究, 2022, 48(1): 49-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJYJ202201004.htmZhang Yan, Zheng Heyun, Ge Liming. The impact of sustainable development policy of resource-based cities on carbon emissions[J]. Journal of Finance and Economics, 2022, 48(1): 49-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJYJ202201004.htm [11] 武祯妮, 尹应凯. 大气污染防治行动打好了资源型城市的"蓝天保卫战"吗?[J]. 产业经济研究, 2022(1): 43-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJJ202201004.htmWu Zhenni, Yin Yingkai. Has the air pollution prevention and control action performed well in the "blue sky defense war" of resource-based cities?[J]. Industrial Economics Research, 2022(1): 43-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJJ202201004.htm [12] 傅佳莎, 浦正宁, 蔡轩. 资源型城市转型政策实施效果评价: 基于PSM-DID方法[J]. 环境经济研究, 2019, 4(1): 108-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJN201901009.htmFu Jiasha, Pu Zhengning, Cai Xuan. Evaluation on the implementation effect of resource-based cities' transformation policy: based on a PSM-DID method[J]. Journal of Environmental Economics, 2019, 4(1): 108-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJN201901009.htm [13] 段存儒, 曾贤刚. 中国资源型城市转型对劳动力需求的影响[J]. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36(3): 606-617. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZX202103006.htmDuan Cunru, Zeng Xiangang. The effect of transformation of resource-based cities on labor demand in China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2021, 36(3): 606-617. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZX202103006.htm [14] Cutter S L, Barnes L, Berry M, et al. A place-based model for understanding community resilience to natural disasters[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2008, 18(4): 598-606. [15] Lam N S N, Qiang Y, Arenas H, et al. Mapping and assessing coastal resilience in the Caribbean region[J]. Cartography and Geographic Information Science, 2015, 42(4): 315-322. [16] 朱金鹤, 孙红雪. 中国三大城市群城市韧性时空演进与影响因素研究[J]. 软科学, 2020, 34(2): 72-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XUXI202002012.htmZhu Jinhe, Sun Hongxue. Research on spatial-temporal evolution and influencing factors of urban resilience of China's three metropolitan agglomerations[J]. Soft Science, 2020, 34(2): 72-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XUXI202002012.htm [17] 孙亚南, 尤晓彤. 城市韧性的水平测度及其时空演化规律——以江苏省为例[J]. 南京社会科学, 2021(7): 31-40, 48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJSH202107004.htmSun Yanan, You Xiaotong. The measure of urban resilience and its spatio-temporal evolution: a case study of Jiangsu province[J]. Nanjing Journal of Social Sciences, 2021(7): 31-40, 48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NJSH202107004.htm [18] 宋宗宇, 李南枢. 基于复合空间视角的超大城市韧性建设路径思考[J]. 北京行政学院学报, 2021(6): 49-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZXY202106006.htmSong Zongyu, Li Nanshu. Thinking of path of the resilience of a megacity in a hybrid space[J]. Journal of Beijing Administration Institute, 2021(6): 49-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZXY202106006.htm [19] 蓝煜昕, 张雪. 社区韧性及其实现路径: 基于治理体系现代化的视角[J]. 行政管理改革, 2020(7): 73-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZGL202007011.htmLan Yuxin, Zhang Xue. Community resilience and its realization path: from the perspective of governance system modernization[J]. Administration Reform, 2020(7): 73-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XZGL202007011.htm [20] Yang D W, Gao X L, Xu L X, et al. Constraint-adaptation challenges and resilience transitions of the industry-environmental system in a resource-dependent city[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2018, 134: 196-205. [21] 唐宇, 宋永永, 薛东前, 等. 资源型城市经济韧性时空演变与障碍因素——以山西省为例[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(5): 53-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202205008.htmTang Yu, Song Yongyong, Xue Dongqian, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution of economic resilience of resource-based cities in Shanxi province and its obstacles[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(5): 53-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202205008.htm [22] Romanelli E, Khessina O M. Regional industrial identity: cluster configurations and economic development[J]. Organization Science, 2005, 16(4): 344-358. [23] Assarkhaniki Z, Rajabifard A, Sabri S. The conceptualisation of resilience dimensions and comprehensive quantification of the associated indicators: a systematic approach[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2020, 51: 101840. [24] 卢盛峰, 董如玉, 叶初升. "一带一路"倡议促进了中国高质量出口吗?来自微观企业的证据[J]. 中国工业经济, 2021(3): 80-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYY202103006.htmLu Shengfeng, Dong Ruyu, Ye Chusheng. Does "the Belt and Road initiative" promote high-quality exports: evidence from firms in China[J]. China Industrial Economics, 2021(3): 80-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYY202103006.htm [25] 严兵, 谢心荻, 张禹. 境外经贸合作区贸易效应评估: 基于东道国视角[J]. 中国工业经济, 2021(7): 119-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYY202107008.htmYan Bing, Xie Xindi, Zhang Yu. Evaluation of trade effect of overseas economic and trade cooperation zone: from the perspective of the host country[J]. China Industrial Economics, 2021(7): 119-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGYY202107008.htm [26] 安礼伟, 蒋元明. 长三角区域规划与先进制造业企业全要素生产率: 基于PSM-DID模型的经验研究[J]. 产业经济研究, 2020(4): 45-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJJ202004004.htmAn Liwei, Jiang Yuanming. Yangtze River Delta regional planning and total factor productivity of advanced manufacturing enterprises: an empirical study based on the PSM-DID model[J]. Industrial Economics Research, 2020(4): 45-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJJ202004004.htm [27] 王慧玲, 孔荣. 正规借贷促进农村居民家庭消费了吗? 基于PSM方法的实证分析[J]. 中国农村经济, 2019(8): 72-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNJJ201908005.htmWang Huiling, Kong Rong. Does formal lending promote rural households' consumption? An empirical analysis based on PSM method[J]. Chinese Rural Economy, 2019(8): 72-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNJJ201908005.htm [28] Heckman J J, Ichimura H, Todd P. Matching as an econometric evaluation estimator[J]. The Review of Economic Studies, 1998, 2: 261-294. [29] 张明斗, 冯晓青. 中国城市韧性度综合评价[J]. 城市问题, 2018(10): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSWT201810004.htmZhang Mingdou, Feng Xiaoqing. Comprehensive evaluation on Chinese cities' resilience[J]. Urban Problems, 2018(10): 27-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSWT201810004.htm [30] 白立敏, 修春亮, 冯兴华, 等. 中国城市韧性综合评估及其时空分异特征[J]. 世界地理研究, 2019, 28(6): 77-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDJ201906009.htmBai Limin, Xiu Chunliang, Feng Xinghua, et al. A comprehensive assessment of urban resilience and its spatial differentiation in China[J]. World Regional Studies, 2019, 28(6): 77-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDJ201906009.htm [31] Mihunov V V, Lam N S N, Rohli R V, et al. Emerging disparities in community resilience to drought hazard in south-central United States[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2019, 41(5): 101302. [32] 武永超. 智慧城市建设能够提升城市韧性吗?一项准自然实验[J]. 公共行政评论, 2021, 14(4): 25-44, 196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGXZ202104003.htmWu Yongchao. Can smart city construction improve urban resilience? A quasi-natural experiment[J]. Journal of Public Administration, 2021, 14(4): 25-44, 196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGXZ202104003.htm [33] 刘成杰, 胡钰苓, 李虹桥, 等. 中国智慧城市试点政策对城市发展质量的影响: 基于韧性发展的视角[J]. 城市问题, 2021(11): 79-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSWT202111010.htmLiu Chengjie, Hu Yuling, Li Hongqiao, et al. The impact of smart city pilot policies on the quality of urban development in China: based on the perspective of resilient development[J]. Urban Problems, 2021(11): 79-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSWT202111010.htm [34] 黄炜, 张子尧, 刘安然. 从双重差分法到事件研究法[J]. 产业经济评论, 2022(2): 17-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDCH202202002.htmHuang Wei, Zhang Ziyao, Liu Anran. From difference-in-differences to event study[J]. Review of Industrial Economics, 2022(2): 17-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDCH202202002.htm [35] 毛成刚, 杨国佐, 范瑞. 数字金融与资源型地区产业结构转型升级——基于109个资源型城市的实证分析[J]. 经济问题, 2022(7): 63-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJWT202207008.htmMao Chenggang, Yang Guozuo, Fan Rui. Digital finance and the transformation and upgrading of industrial structure in resource-based regions: empirical analysis based on 109 resource-based cities[J]. On Economic Problems, 2022(7): 63-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJWT202207008.htm [36] 郑辉, 孙晓华, 龙睿. 资源型城市经济转型的路径与模式[J]. 福建论坛: 人文社会科学版, 2022(1): 61-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJLW202201006.htmZheng Hui, Sun Xiaohua, Long Rui. The path and mode of economic transformation of resource-based cities[J]. Fujian Tribune: The Humanities & Social Sciences Monthly, 2022(1): 61-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJLW202201006.htm -






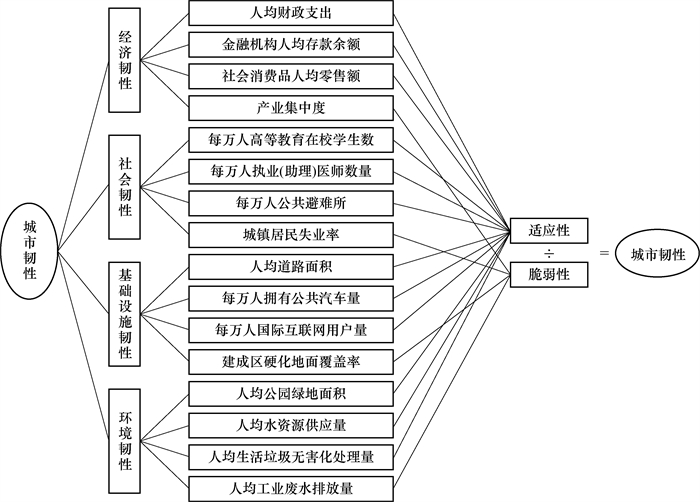
 下载:
下载: