The key causes and characteristics of spontaneous combustion of coal seams affected by igneous intrusion
-
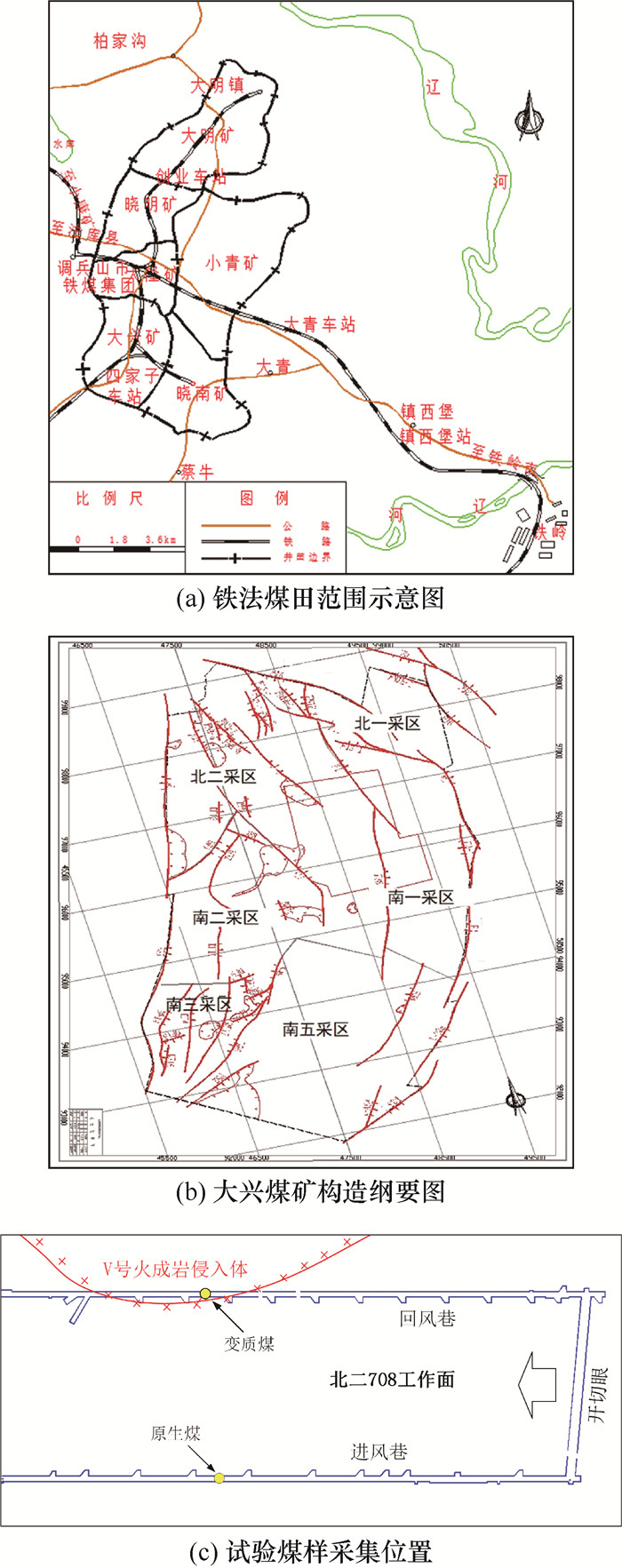
摘要: 为探明火成岩侵蚀导致侵蚀煤层自燃特性变化的关键致因,以受火成岩侵入范围广、煤自然发火严重的铁法煤田大兴煤矿为研究对象,采集火成岩侵蚀形成的变质煤和未受影响的原生煤进行研究。本文利用同步热分析仪、煤自燃特性测定装置等测试了煤样的产热升温特性、气体产生规律、微观结构参数的差异。结果表明,变质煤在低温阶段的放热量较原生煤显著提高,交叉点温度降低了13.2 ℃,更早进入氧化增重阶段;当环境温度超过90 ℃,变质煤的氧化产热与反应速率急速增加,CO和CO2等氧化气体产物生成速率显著升高,表明变质煤的氧化活性高于原生煤;火成岩侵蚀煤层的高温高压作用改变了煤体的孔隙结构,导致煤中有机物质热解与挥发,使得变质煤中的微孔和介孔孔容减小、比表面积降低,宏观孔的孔容达到原生煤的3倍,平均孔径和孔隙率显著增大,有利于氧气分子在煤体内部的输送运移与吸附反应,同时变质煤的含氧官能团较原生煤减少,脂肪烃含量由27.98 % 提高至29.07 %,增强了变质煤的氧化活性。此外,火成岩侵蚀活动导致侵蚀煤层开采时漏风加剧、遗煤氧化时间长、氧化带范围广。火成岩对煤层自然发火内在因素和外在因素的影响,导致侵蚀煤层面临严重的煤自燃灾害。Abstract: In order to find out the key causes of changes in spontaneous combustion characteristics of igneous intrusive coal seams, this paper took the Daxing Coal Mine in Tiefa Coalfield as example for analysis, which was widely invaded by igneous and had serious coal spontaneous combustion disasters.Metamorphic coal and unaffected primary coal were collected from the study area.Specifically, this paper studied the patterns of heat production and temperature rise, gas production rules, and microscopic structure parameters of coal samples by synchronous thermal analyzer and coal spontaneous combustion characteristic measuring device.The experimental results show that the igneous intrusion caused the mutation in the spontaneous combustion characteristics of the coal.Compared with the primary coal, there was significantly higher oxidation heat release of the metamorphic coal at the low temperature stage.Also, the crossing point temperature of metamorphic coal was reduced by 13.2 ℃, and it entered the stage of oxidation and weight gain earlier than the primary coal.When the environment temperature exceeded 90 ℃, the oxidation heat generation and reaction rate of metamorphic coal increased rapidly, which showed higher oxygen consumption rate and faster generation rate of oxidative gas products such as CO and CO2.This demonstrated higher oxidation activity of metamorphic coal than that of primary coal.The analytic results of physicochemical microstructure showed that the high temperature and pressure of igneous intrusion changed the pore structure of coal, which reduced the pore volume and specific surface area of micropores/mesopores in metamorphic coal, and the pore volume of macropores was three times higher than that of primary coal.The average pore size and porosity increased significantly, which was conducive to the transport, migration and adsorption reaction of oxygen molecules in the coal structure.At the same time, igneous intrusion reduced the oxygen-containing functional groups of metamorphic coal, and the content of aliphatic hydrocarbons with higher activity increased from 27.98 % to 29.07 %, which enhanced the oxidative activity of metamorphic coal.Moreover, igneous intrusion caused problems such as increased air leakage, long oxidation time of left coal, and wide oxidation zone during the mining, eventually leading to severe coal spontaneous combustion disasters.
-
表 1 实验煤样工业分析结果
Table 1. Proximate analysis of coal samples
% 煤样 工业分析 镜质组反射率Ro Mad FCad Vad Aad 原生煤 4.70 54.64 32.58 8.08 0.62 变质煤 3.49 64.66 23.43 8.42 1.14 表 2 煤样孔结构特征参数
Table 2. Pore structure parameters of coal samples
煤样 BET比表面积/(m2·g-1) 平均孔径/nm HK微孔孔容/(mm3·g-1) BJK介孔孔容/(mm3·g-1) 原生煤 15.5 4.85 5.05 10.9 变质煤 3.94 7.99 1.19 4.21 表 3 煤样中各主要活性基团谱吸收峰面积占比
Table 3. Infrared absorption peak area proportion of main functional groups in coal
% 煤样 脂肪烃 芳香烃 含氧官能团 矿物 CH3/CH2/CH C=C OH、C=O、COOH等 钙矾石、硫铁矿等 原生煤 27.98 7.09 61.85 3.08 变质煤 29.07 7.17 56.70 7.06 -
[1] Costa M, Moura H, Pinto de Jesus A, et al. Effects of magmatic fluids in coals of são Pedro da cova coalfield, Douro carboniferous basin, Portugal: insights from inorganic geochemistry[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(2): 275. doi: 10.3390/min12020275 [2] Qin Y J, Jin K, Tian F C, et al. Effects of ultrathin igneous sill intrusion on the petrology, pore structure and ad/desorption properties of high volatile bituminous coal: implications for the coal and gas outburst prevention[J]. Fuel, 2022, 316: 123340. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123340 [3] Stewart A K, Massey M, Padgett P L, et al. Influence of a basic intrusion on the vitrinite reflectance and chemistry of the Springfield(No. 5)coal, Harrisburg, Illinois[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2005, 63(1/2): 58-67. [4] 闫浩, 张吉雄, 张强, 等. 巨厚火成岩下采动覆岩应力场-裂隙场耦合演化机制[J]. 煤炭学报, 2016, 41(9): 2173-2179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201609005.htmYan Hao, Zhang Jixiong, Zhang Qiang, et al. Coupling evolution mechanism of mining-induced overlying strata stress field and crack field under extremely thick igneous rock[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2016, 41(9): 2173-2179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201609005.htm [5] 王亮, 郭海军, 程远平, 等. 岩浆岩环境煤层瓦斯异常赋存特征与动力灾害防控关键技术[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(3): 1244-1259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202203018.htmWang Liang, Guo Haijun, Cheng Yuanping, et al. Abnormal coal seam gas occurrence characteristics and the dynamic disaster control technologies in the magmatic rock intrusion area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(3): 1244-1259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202203018.htm [6] 吴斌, 孟凡彬. 岩浆岩侵入煤层的地震属性识别技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2020, 48(6): 64-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.06.009Wu Bin, Meng Fanbin. Seismic attribute recognition technology of magmatic rock intrusive coal seam[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2020, 48(6): 64-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2020.06.009 [7] 蒋静宇. 岩浆岩侵入对瓦斯赋存的控制作用及突出灾害防治技术: 以淮北矿区为例[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2012. [8] Shi Q L, Qin B T, Liang H J, et al. Effects of igneous intrusions on the structure and spontaneous combustion propensity of coal: a case study of bituminous coal in Daxing Mine, China[J]. Fuel, 2018, 216: 181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2017.12.012 [9] Bulguroglu M E, Milkov A V. Thickness matters: Influence of dolerite sills on the thermal maturity of surrounding rocks in a coal bed methane play in Botswana[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 111: 219-229. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.08.016 [10] 代世峰, 任德贻, 刘建荣, 等. 河北峰峰矿区煤中微量有害元素的赋存与分布[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2003, 32(4): 358-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2003.04.004Dai Shifeng, Ren Deyi, Liu Jianrong, et al. Occurrence and distribution of minor toxic elements in coals of Fengfeng coalfield, Heibei Province, North China[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2003, 32(4): 358-362. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2003.04.004 [11] Liu J J, Dai S F, Song H J, et al. Geological factors controlling variations in the mineralogical and elemental compositions of Late Permian coals from the Zhijin-Nayong Coalfield, western Guizhou, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2021, 247: 103855. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2021.103855 [12] Mastalerz M, Drobniak A, Schimmelmann A. Changes in optical properties, chemistry, and micropore and mesopore characteristics of bituminous coal at the contact with dikes in the Illinois Basin[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2009, 77(3/4): 310-319. [13] Jiang J Y, Cheng Y P, Wang L, et al. Petrographic and geochemical effects of sill intrusions on coal and their implications for gas outbursts in the Wolonghu Mine, Huaibei Coalfield, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2011, 88(1): 55-66. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2011.08.007 [14] Şenel İ G, Gürüz A G, Yücel H, et al. Characterization of pore structure of Turkish coals[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2001, 15(2): 331-338. [15] Bu Y C, Niu H Y, Wang H Y, et al. Study on pore structure change and lean oxygen re-ignition characteristics of high-temperature oxidized water-immersed coal[J]. Fuel, 2022, 323: 124346. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124346 [16] 高琳, 莫琼, 廖俊杰, 等. 物化结构对胜利褐煤自燃倾向性的影响[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2021, 52(4): 571-577. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYGY202104010.htmGao Lin, Mo Qiong, Liao Junjie, et al. Effect of physical and chemical structure of shengli lignite on its spontaneous combustion tendency[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021, 52(4): 571-577. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TYGY202104010.htm [17] Golab A N, Carr P F. Changes in geochemistry and mineralogy of thermally altered coal, upper hunter valley, Australia[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2004, 57(3/4): 197-210. [18] 衣刚. 大兴矿N2-706工作面采空区瓦斯与自燃灾害耦合研究[D]. 阜新: 辽宁工程技术大学, 2013. [19] 王亮, 杨良伟, 王瑞雪, 等. 岩浆岩床下伏煤层采空区煤自燃致灾机制与防治[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(1): 125-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201901053.htmWang Liang, Yang Liangwei, Wang Ruixue, et al. Disaster occurred mechanism and prevention of coal spontaneous combustion in goaf of seam under magmatic rock bed[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(1): 125-131. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTKJ201901053.htm [20] 唐辉. 火成岩侵入条件下煤体微观结构变化研究[J]. 煤矿安全, 2022, 53(5): 46-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKAQ202205008.htmTang Hui. Study on changes of coal microstructure under the condition of igneous rock intrusion[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(5): 46-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKAQ202205008.htm [21] 金永飞, 张光, 郭军, 等. 硅化作用对煤低温氧化特性参数的影响规律[J]. 煤矿安全, 2022, 53(1): 31-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKAQ202201005.htmJin Yongfei, Zhang Guang, Guo Jun, et al. The influence of silicification on coal low-temperature oxidation characteristic parameters[J]. Safety in Coal Mines, 2022, 53(1): 31-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MKAQ202201005.htm [22] 周西华, 牛玉平, 白刚. 供风量对褐煤自燃特性参数影响的实验研究[J]. 矿业安全与环保, 2020, 47(1): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ENER202001007.htmZhou Xihua, Niu Yuping, Bai Gang. Experimental study on the influence of air supply on characteristics of lignite spontaneous combustion[J]. Mining Safety & Environmental Protection, 2020, 47(1): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ENER202001007.htm [23] Karsner G G, Perlmutter D D. Reaction regimes in coal oxidation[J]. AIChE Journal, 1981, 27(6): 920-927. [24] Meng X L, Gao M Q, Chu R Z, et al. Multiple linear equation of pore structure and coal-oxygen diffusion on low temperature oxidation process of lignite[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 24(6): 818-823. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1004954116304347 [25] Kaji R, Hishinuma Y, Nakamura Y. Low temperature oxidation of coals: effects of pore structure and coal composition[J]. Fuel, 1985, 64(3): 297-302. [26] 李庆钊, 赵长遂, 陈晓平, 等. O2/CO2气氛燃煤半焦孔隙特性分析[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2009, 30(9): 1605-1608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB200909049.htmLi Qingzhao, Zhao Changsui, Chen Xiaoping, et al. Analysis of pore structure in coal char obtained in an O2/CO2 environment[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2009, 30(9): 1605-1608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCRB200909049.htm [27] Ma L Y, Zhang L, Wang D M, et al. Pore structure evolution during lean-oxygen combustion of pyrolyzed residual from low-rank coal and its effect on internal oxygen diffusion mechanism[J]. Fuel, 2022, 319: 123850. [28] 褚廷湘, 杨胜强, 孙燕, 等. 煤的低温氧化实验研究及红外光谱分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2008, 18(1): 171-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK200801032.htmChu Tingxiang, Yang Shengqiang, Sun Yan, et al. Experimental study on low temperature oxidization of coal and its infrared spectrum analysis[J]. China Safety Science Journal: CSSJ, 2008, 18(1): 171-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK200801032.htm [29] Dai S F, Ren D Y. Effects of magmatic intrusion on mineralogy and geochemistry of coals from the Fengfeng-Handan coalfield, Hebei, China[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2007, 21(3): 1663-1673. [30] Sujanti W, Zhang D. A laboratory study of spontaneous combustion of coal: the influence of inorganic matter and reactor size[J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(5): 549-556. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236198001884 [31] Sujanti W, Zhang D K. Investigation into the role of inherent inorganic matter and additives in low-temperature oxidation of a Victorian brown coal[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2000, 152(1): 99-114. [32] 许家林, 钱鸣高, 金宏伟. 岩层移动离层演化规律及其应用研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2004, 26(5): 632-636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200405011.htmXu Jialin, Qian Minggao, Jin Hongwei. Study and application of bed separation distribution and development in the process of strata movement[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2004, 26(5): 632-636. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200405011.htm -






 下载:
下载: